
The most probable region of electron rotation around the nucleus is called the orbital. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. Electron configuration of sodium through orbitalĪtomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through the orbital diagrams. The electron configuration of an element with an atomic number greater than 18 cannot be properly determined according to the Bohr atomic model. Electrons can be arranged correctly through orbits from elements 1 to 18. Therefore, the order of the number of electrons in each shell of the sodium atom is 2, 8, 1. Therefore, a sodium atom will have two electrons in the first shell, eight in the 2nd orbit, and an electron in the 3rd shell. That is, the number of electrons in sodium is 11. The atomic number is the number of electrons in that element. Therefore, the maximum electron holding capacity in the first shell is two, the second shell is eight and the 3rd shell can have a maximum of eighteen electrons. The maximum electrons holding capacity in N orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 4 2 = 32. The maximum electrons holding capacity in M orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 3 2 = 18. The maximum electron holding capacity in L orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 2 2 = 8. The maximum electron holding capacity in K orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 1 2 = 2.

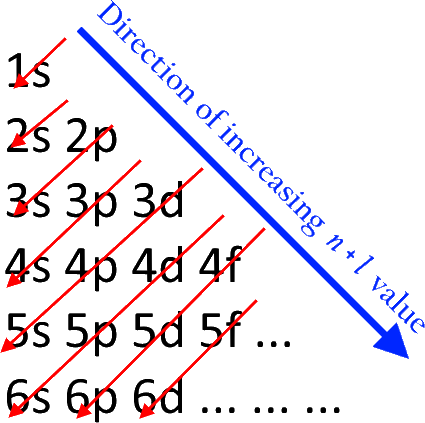
The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n 2. K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, and N is the name of the fourth orbit. These circular paths are called orbit(shell). The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. The complete idea of the orbit is given there. Scientist Niels Bohr was the first to give an idea of the atom’s orbit. Sodium electron configuration through orbit For example Aufbau principle, Hund’s principle, and Pauli’s exclusion principle. Sodium(Na) electron configuration (Bohr model)Įlectron configuration through orbitals follows different principles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
